| Strain Name |
NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Bcgen Fahtm1Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name |
B-NDG Fah KO mice |
| Background | B-NDG | Catalog number | 112959 |
|
Related Genes |
NA |
||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
2184 | ||
- Fah is the final enzyme in the tyrosine metabolism pathway, primarily expressed in the liver and kidneys. Deficiency of FAH is associated with Type 1 hereditary tyrosinemia (HT). As a result of the severe liver damage induced by Fah knockout (KO), this mouse model allows for the reconstruction of a functional human liver utilizing primary human hepatocytes.
- Gene editing strategy: The exons 2-14 of mouse Fah gene were knocked out in B-NDG Fah KO mice.
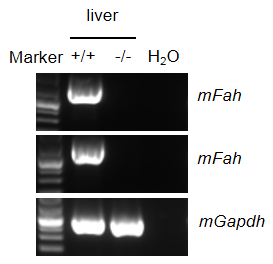
- mRNA expression analysis: Mouse Fah mRNA were detectable only in B-NDG mice but not in homozygous B-NDG Fah KO mice.
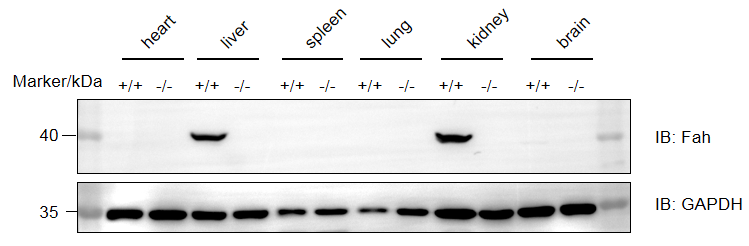
- Protein expression analysis: Fah was only detected in liver and kidney of B-NDG mice but not in homozygous B-NDG Fah KO mice.
- Liver damage analysis: After removing NTBC drinking water from B-NDG Fah KO mice for three weeks, blood biochemical analysis revealed an increase in ALT, AST and ALP levels, while ALB levels decreased. Additionally, HE staining results indicated that the mice had developed liver damage.
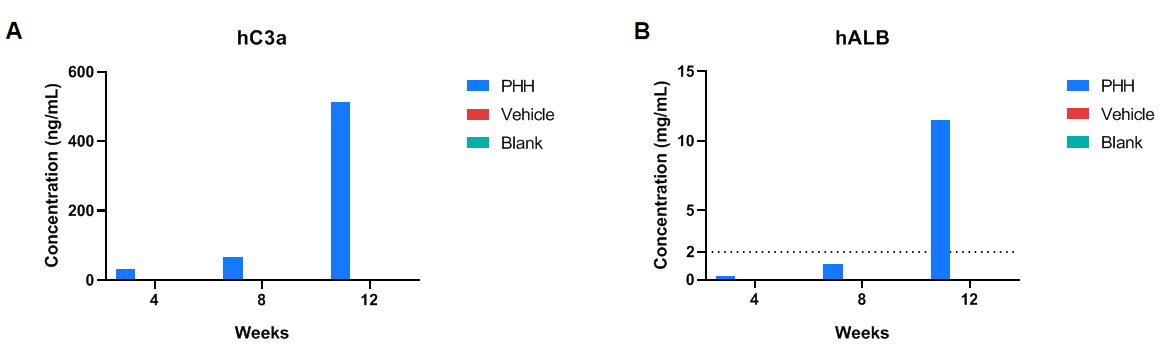
- Hepatocyte transplantation analysis: The levels of human FAH and human CK18 gradually increased in the livers of B-NDG Fah KO mice following the transplantation of human hepatocytes. Concurrently, the serum levels of human C3a and human albumin in the mice progressively rose.
- Application: This product is used for human hepatocytes transplantation and for evaluating the efficacy and safety of drugs associated with liver diseases.
mRNA expression analysis in B-NDG Fah KO mice
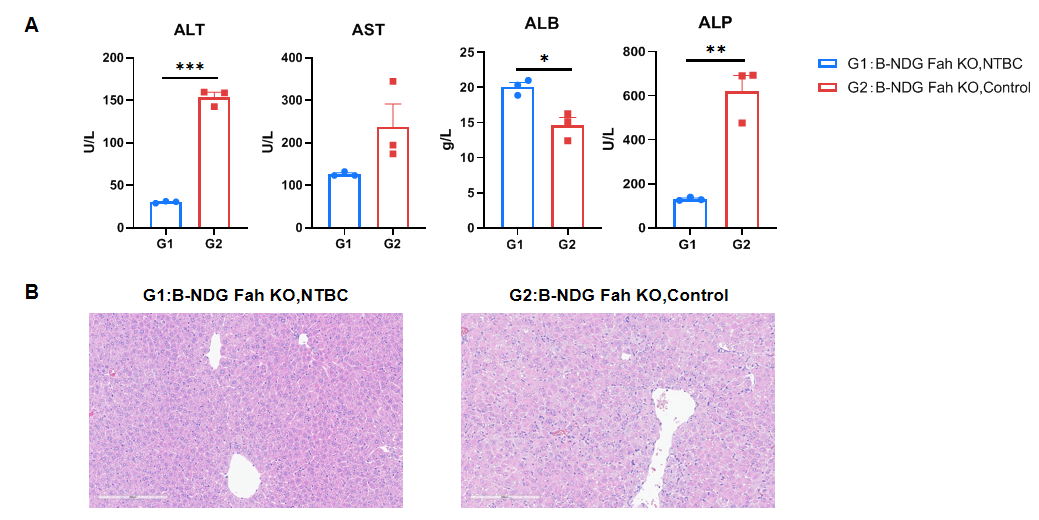
Liver damage analysis in B-NDG Fah KO mice. After removing NTBC drinking water from B-NDG Fah KO mice for three weeks, blood biochemical analysis revealed an increase in ALT, AST and ALP levels, while ALB levels decreased. Additionally, HE staining results indicated that the mice had developed liver damage. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by One-way or Two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Human FAH in liver
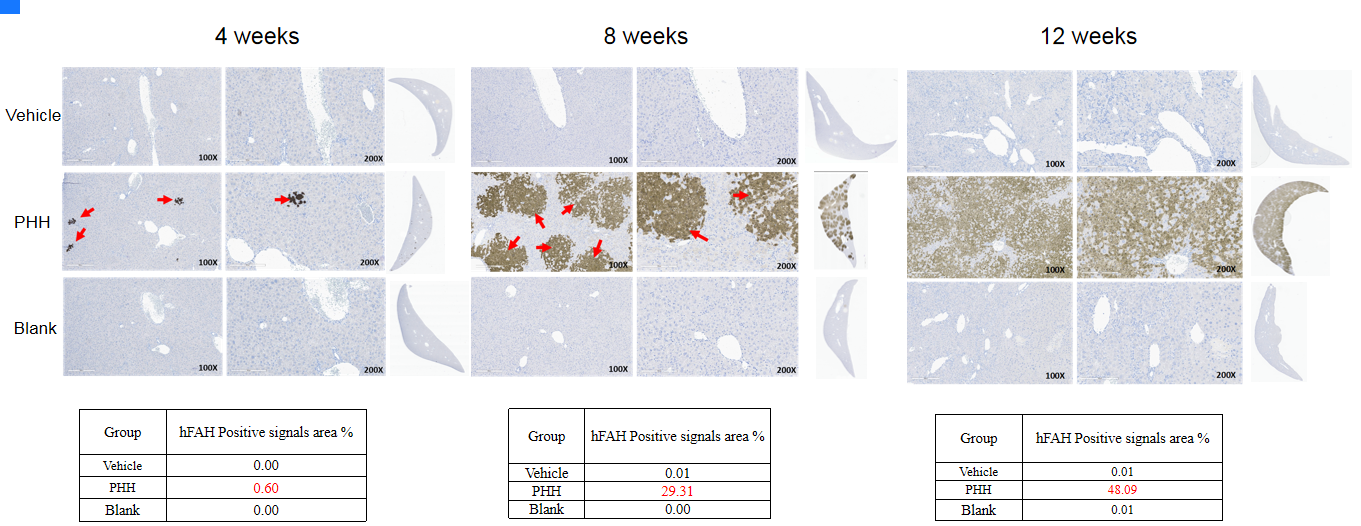
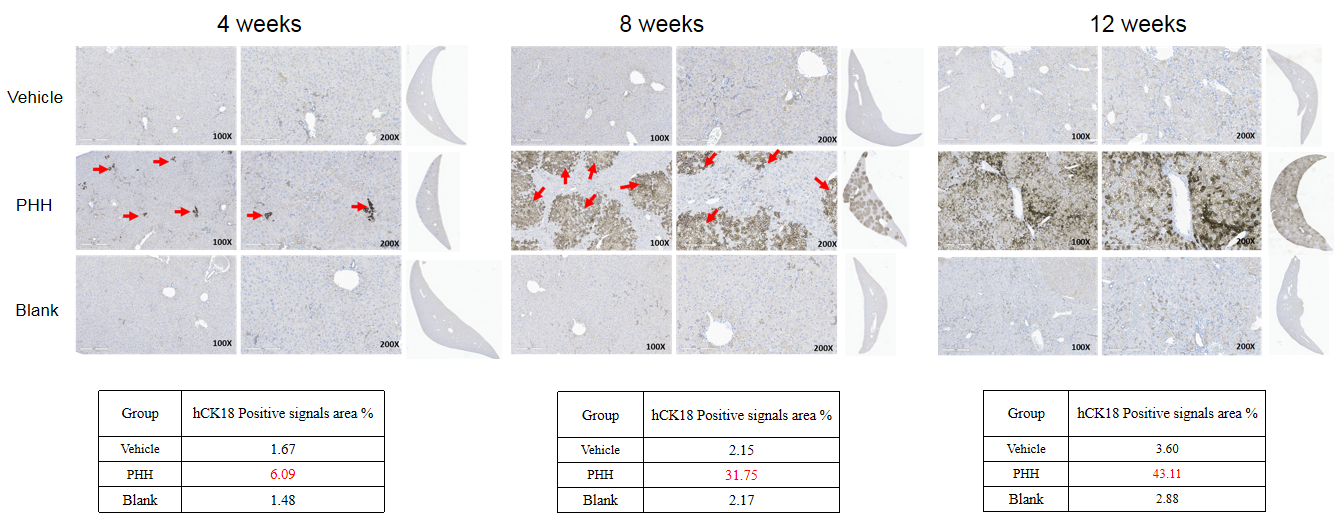
Note: Vehicle (Sham-operated group); PHH (Primary Human Hepatocytes); Blank (Without any treatment). The levels of human CK18 gradually increased in the livers of B-NDG Fah KO mice following the transplantation of human hepatocytes. The sections were scanned with a Leica Aperio GT450 scanner, and the staining positive area was analyzed using the HALO area quantification algorithm.